Nukes are still a thing

On the 21st of July 2023, the movie Oppenheimer released in cinemas around the world. The movie is about J. Robert Oppenheimer, who is often called the father of the atomic bomb. The movie details how Oppenheimer got involved in the so-called Manhattan project, America’s secret project to develop the world’s first nuclear bomb, and how the development of the bomb went. The movie also has two other plots detailing what happened after the second world war and how Oppenheimer got shunned for not wanting to develop a hydrogen bomb. This movie released in a period of rising global tensions and is, to me, a very important piece about the dangers of having weapons of mass destruction available at will to multiple global superpowers. But what was the context of the creation of the first nuclear bomb, how does it compare to the current state of geopolitical affairs, and why is Oppenheimer such an important movie?
The first ever instance of nuclear fission was achieved in December of 1938 in Berlin, when chemists Otto Hahn and Fritz Strassman bombarded uranium with slow neutrons and discovered Barium had been produced. This discovery led physicists Lise Meitner and Otto Robert Frisch to theorize and proof the process of nuclear fission. Nuclear fission occurs when heavy nuclides split into lighter nuclides, in which case a large amount of energy is released. The first discovered, and most well-known version of nuclear fission is when Uranium-235 is shot with a neutron to make Uranium-236, which splits into Barium, Krypton and three more neutrons. It also releases a large amount of energy. The additional neutrons released in the reaction is what allows the chain reaction which means more nuclides will split which releases even more energy and so on.
The energy released from nuclear fission can be used to create nuclear bombs. A large amount of nuclear material will react with exponentially growing speed, which will release an energy equivalence between 1 and 500.000 tons of TNT. The first ever successful nuclear detonation was called Trinity, and was achieved on the 16th of July 1945 in the desert of New Mexico in the United States. It was measured to be roughly 20 kilotons of TNT.

In August 1945, near the end of the second world war. Germany had already surrendered unconditionally to the Allies, but Japan was still actively fighting the war against the United States. The U.S. Government was planning ‘Operation Downfall’ to invade the Japanese mainland and force them to surrender. It was calculated that this operation would result in the deaths of roughly one million U.S. soldiers, and many more Japanese soldiers and civilians. Because Soviet Union was also planning to declare war on Japan, the U.S. government was afraid the Soviet Union would end up getting more influence in post-war Japan than the Americans. To ensure their influence, and to spare U.S. lives, the U.S. government decided to use the newly developed nuclear bombs to attempt to force the Japanese government into an unconditional surrender. On August 6th 1945, the first nuclear bomb was dropped on Hiroshima, then on August 9th a second nuke was dropped on Nagasaki. The nuclear bombs, combined with the Soviet invasion of Manchuria which started on August 9th was enough to make the Japanese government surrender unconditionally, with American influence guaranteed. This use of nuclear bombs is the only time nukes were ever used in active conflict and cost between 129.000 and 226.000 lives.
The use of nuclear bombs, combined with the Soviets detonating their first nuclear bomb on the 29th of August kicked off a period in history known as the Cold War. Both the U.S. and the Soviet Union wanted to be the largest and most powerful countries in the world and make their respective ideologies, communism and capitalism, the standard world ideology. But open conflict was not an option anymore as nuclear bombs would mean total destruction for both sides. One of the ways the countries measured power was by stockpiling nuclear bombs. The period of 1950 to 1990 saw an exponential growth of the total amount of nuclear weapons in the possession of both the U.S. and the Soviet Union from hundreds to tens of thousands of nuclear bombs each. 1952 also saw the successful detonation of ‘Ivy Mike’ the first ever thermonuclear bomb. A type of nuke that uses nuclear fusion instead of nuclear fission, which creates a blast at least ten times as powerful. The largest stockpiles of nuclear bombs was in 1985, when the total amount of warheads on the planet reached over 60000 warheads.
However, the late 80’s and early 90’s saw a significant decrease in Cold War tensions. Germany, which had been split into an eastern and western state, reunified into a single state again. The Iron Curtain, a strongly fortified border wall between east and west Europe, became more open. And when on the 25th of December 1991 the Soviet Union dissolved, the Cold War was considered over.
The Cold War has been considered to be over ever since, but now, in the 2020’s geopolitical tensions are once more rising. The speed at which warheads are being decommissioned is reducing. In 2024, the number of deployed warheads has increased for the first time in multiple decades. The number of major armed conflicts and wars around the world is also on the rise again, most famously with the war between Russia and the Ukraine, which is the first open conflict in Europe in more than two decades. During this war, Russia has threatened to use nuclear weapons in case the war does not go in their favor. The U.S. has responded to this by saying that they will use nuclear weapons if Russia decides to use nuclear weapons. Tensions between China and the U.S. are also rising, with multiple instances of the two countries trying to undercut each other in ways which are very reminiscent of the Cold War.
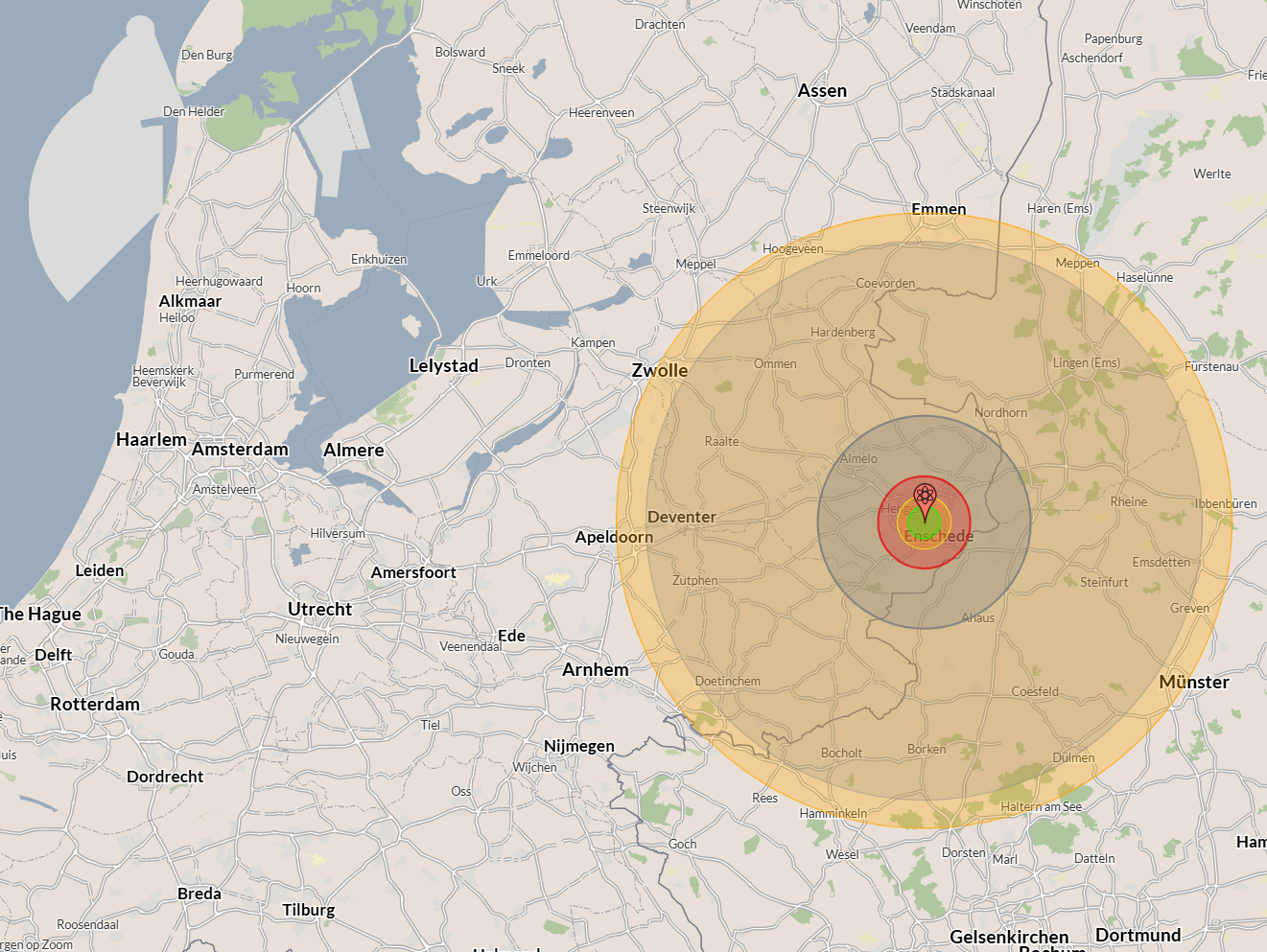
The consequences of nuclear launch are bigger than most people can even imagine. NukeMap, a free online resource which allows people to compare the size of a nuclear blast over a map, can show what would happen if a nuke hits a specific spot. If it is used to compare the effect of blast radius of the ‘Tsar Bomba’ the biggest nuclear weapon ever detonated against the Universiteit Twente campus, the true size of the destruction becomes painfully clear. As long as nuclear weapons exist, it is important to remain thoughtful of them.
It is in this context that the 2023 movie Oppenheimer shows theaters how the nuclear bomb came to be, and how it could mean the end of the world if they are ever dropped. As the fear of nuclear annihilation and the activism against the increase of the nuclear stockpile has mostly gone down together with the Cold War, the movie is an important reminder that nuclear weapons are still very much present, and the potential use of nuclear weapons is never excluded. In a heavy hitting ending scene, Oppenheimer imagines a future nuclear war, from the launch of thousands of rockets with warheads on them, to the entire world burning.
References
[1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Historical_nuclear_weapons_stockpiles_and_nuclear_tests_by_country
[2] https://nuclearsecrecy.com/nukemap/